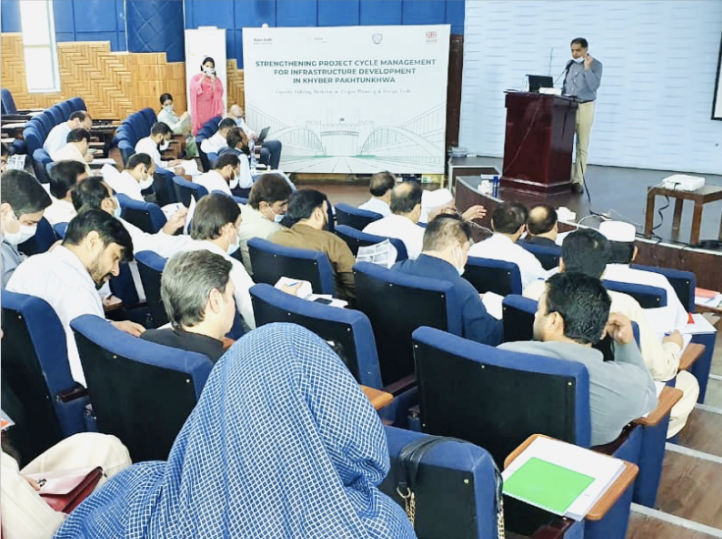
OVERVIEW
SEED is assisting the Planning & Development (P&D) Department and the Communication and Works (C&W) Department of KP to enhance its technical capacity for managing infrastructure project cycles – planning, implementation, and monitoring – more efficiently and effectively. Infrastructure projects represent 75 per cent of the KP’s annual budget, and SEED has identified critical gaps within the existing processes that lead to inefficient resource allocation and outcomes. Diverse interventions have been proposed to update and streamline the current planning systems for efficient planning, effective implementation and monitoring.